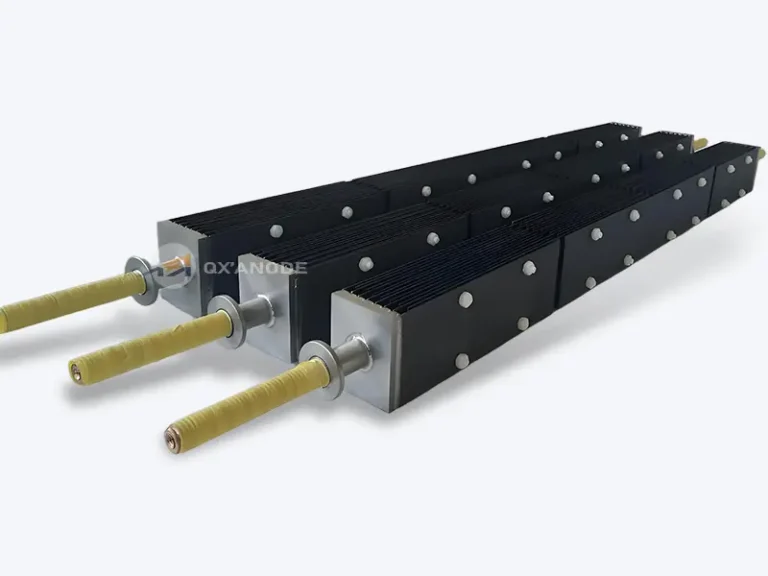
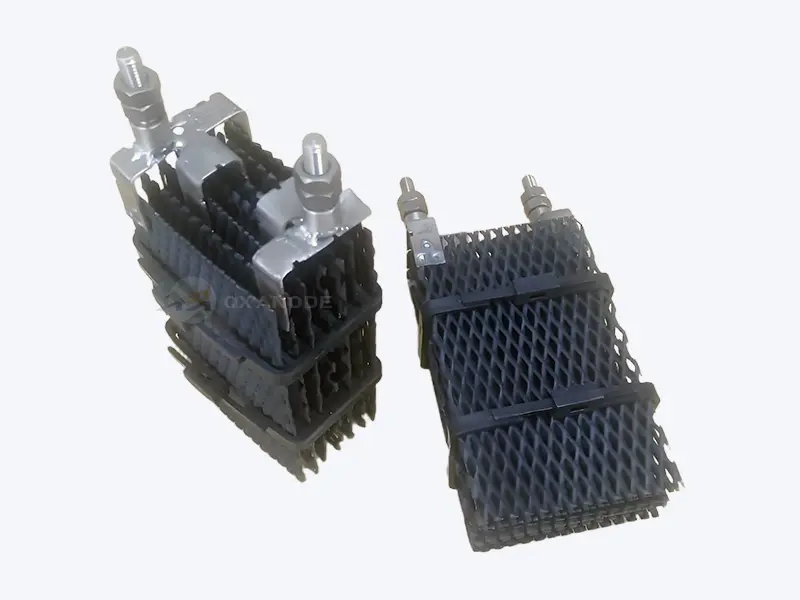
The Titanium anode for salt chlorinator, as the core component of the swimming pool salt chlorination generator system, exhibits significant differences in the efficiency of electrolytic chlorine production in different types of swimming pool water. The chlorine evolution current efficiency of titanium anodes for salt chlorinators can reach more than 90% under different water quality conditions such as household swimming pools, public swimming pools, hot spring swimming pools, and outdoor swimming pools, but the efficiency will decrease significantly in complex water quality environments.
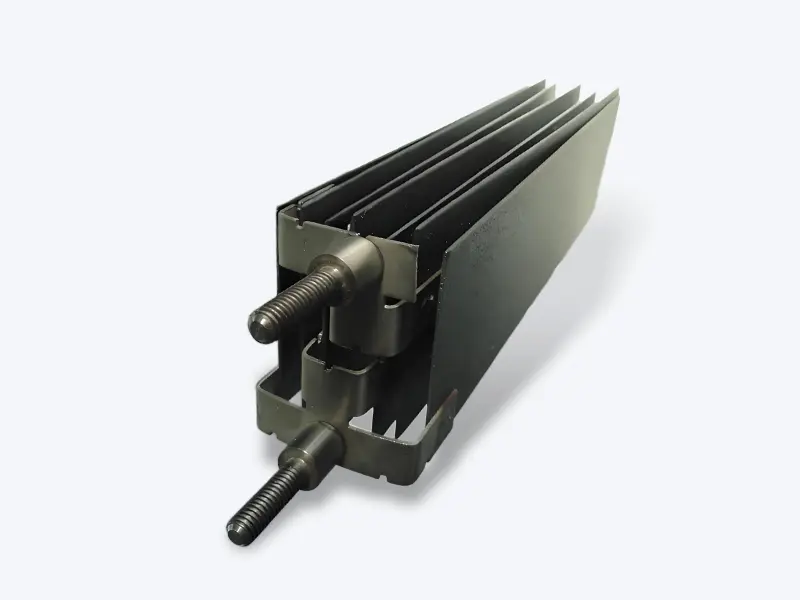
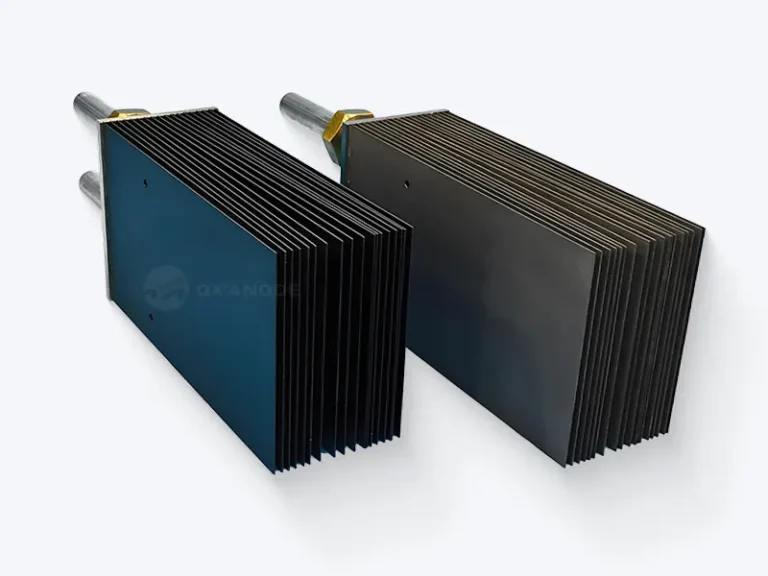
Titanium anodes for salt chlorine generators serve as the core component of the salt chlorine generator system, and their performance directly determines the efficiency and stability of the entire system. Titanium anodes typically use Grade 1 or Grade 2 pure titanium as the substrate, with a surface coated with mixed metal oxide (MMO) coatings such as ruthenium-iridium oxide. They generate disinfecting components like hypochlorous acid through electrolytic reactions in salt-containing water.
With the continuous improvement of people’s requirements for water quality safety, swimming pool water disinfection technology is developing towards the direction of high efficiency, safety and environmental protection. Although traditional chemical disinfection methods have reliable effects, they have problems such as transportation and storage risks and the generation of by-products. In contrast, the salt chlorine generator technology, which generates disinfectants on-site by electrolyzing salt water, has the advantages of safe operation, low cost, and no harmful by-products, and is gradually becoming the mainstream technology for swimming pool disinfection.
Classification System of Swimming Pool Water Quality and Titanium Anode Salt Chlorine Generator
1.Classification Standards and Characteristics of Swimming Pool Water Quality
According to relevant international standards, the swimming pool water quality classification system is mainly divided based on factors such as purpose, environment, and water source.
Classification by purpose
- competition swimming pool
- Training pool
- diving pool
- Children’s swimming pool
as well as general-purpose swimming pools such as entertainment pools and leisure pools. Classified by environment, they mainly include two categories: indoor swimming pools and outdoor swimming pools. Among them, outdoor swimming pools can be further divided into above-ground and underground types.

Standard parameter for swimming pool water quality
- PH value: 7.2-7.8
- Residual chlorine concentration: 0.3-1.0mg/L
- Turbidity: not exceeding 0.5 NTU
- Water temperature range: 20-30℃
- Total alkalinity: 80-120ppm
- Calcium hardness: 200-400ppm
The water quality characteristics of special types of swimming pools are more complex. The water temperature of hot spring swimming pools is usually 38-42℃, with a mineralization degree of up to 1.676-10.056g/L, and they contain rich mineral components; the salt concentration of seawater swimming pools is as high as 30000-35000mg/L, which is much higher than that of ordinary saltwater swimming pools; the calcium hardness of high-hardness swimming pools can exceed 500mg/L, which is prone to scaling; and due to the large number of people, public swimming pools have significantly higher levels of organic matter and bacteria than other types of swimming pools.
2.Basic Principles and Performance Parameters of Titanium Anodes for Salt Chlorinators
The basic principle of chlorine production by electrolysis using a titanium anode in a salt-chlorine machine is that, under the action of direct current, an oxidation reaction occurs on the surface of the titanium anode in water containing chloride ions.
Main reaction process
Anode reaction: 2Cl⁻ → Cl₂↑ + 2e⁻
Secondary reaction: Cl₂ + H₂O → HClO + H⁺ + Cl⁻
The hypochlorous acid produced possesses strong oxidizing properties; its redox potential ranges from 650 to 800 mV. It is capable of killing 99.5% of pathogens within 30 seconds, making its disinfection efficiency 60 times that of traditional chlorine-based disinfectants.
Core performance parameters
- Chlorine evolution current efficiency: 80-95%.
- Current density range: 100~1000A/m².
- Chlorine evolution potential: ≤1.14V vs SCE.
- Service life: 2-5 years (depending on usage conditions).
Ideal water quality conditions
- Salt concentration: 3000-5000mg/L.
- PH value: 7.2-7.8.
- Temperature: 25-30℃
- Calcium hardness: 200-400ppm
- Organic matter content: Low
Under ideal water quality conditions, titanium anodes exhibit excellent electrolytic chlorine production performance. In swimming pool water with a salt concentration of 3000-5000mg/L, the chlorine evolution current efficiency of ruthenium-iridium-titanium anodes can stably remain above 95%, the production rate of hypochlorous acid is high, and the residual chlorine concentration can be easily maintained within the safe range of 0.3-0.5mg/L. However, when the water quality conditions change, these performance parameters will fluctuate significantly.
Application of Titanium Anodes for Salt Chlorinators in Small Swimming Pools
1.Application of Titanium Anodes for Salt Chlorinators in Small Swimming Pools
Small swimming pools usually have characteristics such as low foot traffic, less water pollution, and easy control of salt concentration. The salt concentration in such pools is generally stable within the ideal range of 3000-5000mg/L, and the content of impurities such as organic matter, calcium and magnesium ions in the water is low. In such a relatively clean water environment, titanium anodes exhibit the best performance in salt chlorinators.
Data shows that in domestic swimming pool water with a salt concentration of 3500mg/L, a pH value of 7.4, and a water temperature of 25°C, the chlorine evolution current efficiency of the titanium anode used in the salt chlorine generator can reach 99.5%, and the chlorine evolution potential at a current density of 10mA/cm² is only 1.13V vs SCE. This high efficiency is mainly attributed to the fact that in a clean water environment, it is not easy for pollutant deposits to form on the electrode surface, allowing the catalytic activity of the coating to be fully exerted. At the same time, the low impurity content reduces the occurrence of side reactions and improves the current efficiency.
The service life of titanium anodes in small swimming pools is relatively long. Due to stable water quality and mild operating conditions, the service life of ruthenium-iridium-titanium anodes can easily reach more than 2 years. The scaling rate on the electrode surface is extremely slow, and self-cleaning can be achieved through regular polarity reversal, without the need for frequent chemical cleaning.
Small swimming pools also present some special challenges. In some areas, the tap water has high hardness, and long-term use may cause slight scale to form on the surface of the electrodes. When the calcium hardness in the water exceeds 450mg/L, calcium carbonate deposits will appear on the electrode surface, affecting the electrolysis efficiency by approximately 5-10%. In addition, the intermittent operation mode of household swimming pools also has a certain impact on electrode performance, and frequent starts and stops will accelerate the loss of the coating.
2.Application of Titanium Anodes for Salt Chlorinators in Public Swimming Pools
The water quality conditions of public swimming pools are far more complex than those of private swimming pools, mainly reflected in aspects such as large number of people, diverse types of pollutants, and frequent fluctuations in water quality. Such pools not only bring in a large amount of organic substances such as human secretions and residual skin care products, but also experience fluctuations in salt concentration due to frequent water replenishment. At the same time, the contents of calcium and magnesium ions and suspended solids are also significantly higher than those in private swimming pools.
In a public swimming pool environment, titanium anodes used in salt chlorinators face multiple challenges. Firstly, there is the issue of organic matter consumption. Organic pollutants such as sweat, saliva, skin cells, hairspray, and cosmetics react with the chlorine generated through electrolysis to form compounds like chloramines. Although these substances have a chlorine odor, their disinfection ability is very weak.
Next is the issue of impurity deposition. Suspended solids and colloidal substances in public swimming pools tend to adhere to the surface of the electrodes, forming an isolation film that hinders the progress of electrolytic reactions. Especially when the water contains a relatively large amount of heavy metal ions such as iron and manganese, these ions will be oxidized on the surface of the titanium anode used in the salt chlorine generator to form non-conductive oxides, which reduces the activity of the anode coating, increases the voltage drop and power consumption.
Fluctuations in the operating parameters of public swimming pools can also affect the performance of titanium anodes used in salt chlorinators. Due to changes in the number of swimmers, the swimming pool needs to continuously adjust the chlorine dosage, which leads to frequent changes in current density. This increases the proportion of oxygen evolution side reactions and reduces the selectivity of chlorine evolution.
In view of the special environment of public swimming pools, actual operation data shows that the chlorine evolution current efficiency of titanium anodes used in salt chlorinators is usually between 80-90%, requiring more frequent maintenance and cleaning. To maintain a stable disinfection effect, the titanium anode system of public swimming pools usually needs to be equipped with a more powerful filtration system and more frequent water quality monitoring.


3.Application of Titanium Anodes for Salt Chlorinators in Outdoor Swimming Pools
The water quality of outdoor open-air swimming pools is greatly affected by the natural environment. Factors such as temperature, light, and rain can indirectly affect the performance of titanium anode salt chlorinators. Such swimming pools not only have to deal with water temperature fluctuations caused by seasonal changes but also handle issues such as rainwater dilution, dust pollution, and algae growth.
Temperature fluctuations are a major challenge for outdoor swimming pools. During high temperatures in summer, the water temperature can reach above 35°C, at which point the decomposition rate of hypochlorous acid accelerates, requiring the titanium anode of the salt chlorine generator to continuously and efficiently electrolyze to compensate for chlorine loss. When the water temperature rises from 25°C to 35°C, the half-life of hypochlorous acid shortens from approximately 2 hours to 30 minutes, which means the titanium anode of the salt chlorine generator needs to increase chlorine production by 3-4 times to maintain the same residual chlorine level. In low temperatures in winter, the water temperature may drop below 10°C, at which point the active chlorine production rate of the titanium anode will decrease significantly. For every 10°C drop in water temperature, the chlorine evolution current efficiency decreases by about 5-8%, and the current density needs to be increased to meet disinfection requirements.
The impact of light is mainly reflected in two aspects. First, ultraviolet rays will accelerate the decomposition of hypochlorous acid. In strong sunlight, the decomposition rate of hypochlorous acid can be 2-3 times faster than in dark environments. Second, algae will reproduce rapidly under sunlight, consuming nutrients in the water and producing organic matter, which increases the demand for chlorine. Data shows that in eutrophic outdoor swimming pools, the chlorine consumed by organic matter can account for 30-40% of the total chlorine consumption.
In actual operation, the titanium anode system of salt chlorinators for outdoor swimming pools needs to have stronger adaptability. During the high-temperature period in summer, the current density needs to be increased to compensate for the rapid decomposition of chlorine; in winter, the current density needs to be reduced to avoid excessive energy consumption caused by over-electrolysis. To address the issue of rainwater dilution, an automatic salt-adding system needs to be equipped to replenish salt in a timely manner. At the same time, regular electrode cleaning (1-2 times a month) and biofilm removal (once a quarter) are also necessary maintenance measures.
Through reasonable system design and operation management, the titanium anode used in salt-chlorine generators can still maintain good performance in outdoor swimming pools. After being equipped with a complete water quality monitoring and automatic control system, the average chlorine evolution current efficiency of the titanium anode can be maintained at 80-85%.


The influence of water quality on titanium anode for salt chlorinator
Chloride ion concentration
The concentration of chloride ions is the most critical factor determining the effectiveness of chlorine production via electrolysis using titanium anodes in salt-chlorine generators. From the perspective of electrochemical principles, the oxidation reaction of chloride ions on the anode surface is the core of the entire salt-chlorine generator process.
PH value
The influence of pH value on the chlorine production effect of titanium anodes used in salt-chlorine machines through electrolysis is multifaceted. It affects the existing form of chlorine, the selectivity of the chlorine evolution reaction, the chemical environment on the electrode surface, and the chlorination reaction of organic substances.
Temperature
The effect of temperature on the chlorine production efficiency of titanium anodes used in salt-chlorine machines through electrolysis exhibits a dual nature. On one hand, an increase in temperature is beneficial for improving electrolysis efficiency; on the other hand, an increase in temperature also brings about negative effects such as accelerated decomposition of hypochlorous acid.
Impurity
The influence of impurity ions in swimming pool water on the chlorine production effect of titanium anodes used in salt chlorine generators through electrolysis is complex and diverse. These impurity ions include cations such as calcium and magnesium, as well as anions such as sulfate and carbonate.
organic compound
Organic substances in swimming pool water are important factors affecting the chlorine production efficiency of titanium anodes used in salt chlorine generators through electrolysis. These organic substances come from a wide range of sources, including human secretions, cosmetic residues, environmental pollutants, etc.
Optimization of Titanium Anodes for Salt Chlorinators
Improvement of Titanium Anodes for Salt Chlorinators
The improvement of titanium anode coating materials for salt-chlorine generators is a fundamental way to enhance the performance of salt-chlorine generators. Although traditional ruthenium-iridium coatings have excellent performance, they have problems such as large consumption of precious metals, high cost, and insufficient stability in special environments.
The composite coating system is an important development direction. By combining coating materials with different functions, synergistic optimization of performance can be achieved. For example, using a three-layer structure consisting of a platinum metal bottom layer and a ruthenium-iridium oxide surface layer can significantly improve the stability of the electrode in harsh environments. Electrodes with this structure can work stably in the pH range of 2-10, and their service life can also be extended in water bodies containing heavy metal ions.
Gradient coating technology can improve the bonding force between the coating and the titanium anode substrate for salt chlorinators and reduce coating detachment by establishing gradient changes in composition and structure in the titanium anode coating for salt chlorinators. By controlling the gradient change of the ruthenium-iridium ratio in the coating, the adhesion of the coating can be doubled, and the service life can be extended by 20-30%. This coating is suitable for application scenarios that need to withstand temperature cycles.
Optimization of Titanium Anode Structure for Salt-Chlorine Generators
The optimized design of electrode structures is of great significance for improving electrolysis efficiency and reducing energy consumption. Although traditional flat-plate electrodes have a simple structure, they have problems such as low mass transfer efficiency and uneven current distribution.
The porous electrode structure is one of the most representative improvements. By processing pores on the titanium anode substrate for salt chlorinators or using porous titanium materials, the specific surface area of the electrode can be significantly increased. Studies have shown that using a porous titanium electrode with a pore size of 20 microns can increase the specific surface area by 5-10 times, and the electrolysis efficiency can be improved by 20-30% accordingly. The porous structure not only increases the reaction area but also improves the mass transfer process, making the electrolysis reaction more uniform.
The electrode structure further enhances electrode performance. For example, using structures such as titanium mesh and titanium fiber felt can achieve a larger electrode area within a limited space. Using titanium mesh titanium anodes for salt-chlorine generators, under the same volume, the electrode area is approximately 1.2 times larger than that of flat-plate electrodes, and the current density can be increased by 20-30%. At the same time, the titanium mesh structure also has good fluid distribution characteristics, which is beneficial to the escape of bubbles.
The modular electrode design offers greater flexibility. By designing electrodes as standard modules, they can be flexibly combined according to actual needs. For example, the combination of plate and mesh electrodes can meet different application scenarios simultaneously. The modular design also facilitates maintenance and replacement; when a module has a problem, it can be replaced individually without shutting down the entire system for maintenance.
The surface treatment technology of electrodes cannot be ignored either. Pretreating the surface of titanium anodes used in salt chlorinators through methods such as sandblasting and chemical etching can improve the adhesion of the coating and enhance the electrode performance.
Regulation and control of operating parameters of titanium anodes for salt chlorine generators
The optimization of operating parameters is a key measure to improve the efficiency of the chlorine production system using titanium anodes in salt-chlorine machines. The traditional fixed-parameter operation mode cannot adapt to the dynamic changes of water quality, which easily leads to reduced efficiency or increased energy consumption. Intelligent control technology enables the system to always maintain the optimal operating state through real-time monitoring and automatic adjustment.
The control of current density is one of the core technologies. Under different water quality conditions, there exists an optimal range of current density. By monitoring parameters such as residual chlorine concentration, pH value, and electrical conductivity online, the system can automatically adjust the current density, ensuring that the electrolysis efficiency remains above 80% at all times.
Temperature control strategies are crucial for maintaining the stable operation of the system. Controlling the electrolysis temperature within the range of 25-30℃ can achieve the best comprehensive performance. When the water temperature is too high, the cooling system can be used to lower the temperature; when the water temperature is too low, the current density can be appropriately increased to compensate for efficiency losses. For outdoor swimming pools with large temperature fluctuations, frequency conversion control technology can be adopted to automatically adjust operating parameters according to the water temperature.
Precise control of the pH value is of great significance for improving electrolysis efficiency and reducing the formation of by-products. Maintaining the pH value within the range of 7.2-7.6 can ensure disinfection effectiveness while minimizing the generation of by-products such as trihalomethanes. Through online pH monitoring and automatic addition of acid-base regulators, the fluctuation of the pH value can be controlled within ±0.1.
Why Choose Qixin titanium anode
Qixin Titanium is a manufacturer of titanium anodes from China., focusing on the R&D, manufacturing and application of Mixed Metal Oxide (MMO) coated titanium anodes.
Founded in 2006, with over 20 years of manufacturing experience, we provide stable and reliable titanium anode products suitable for multiple scenarios. We help enterprises improve electrolysis efficiency, reduce operating costs, and offer personalized customization to ensure long-term stable operation.