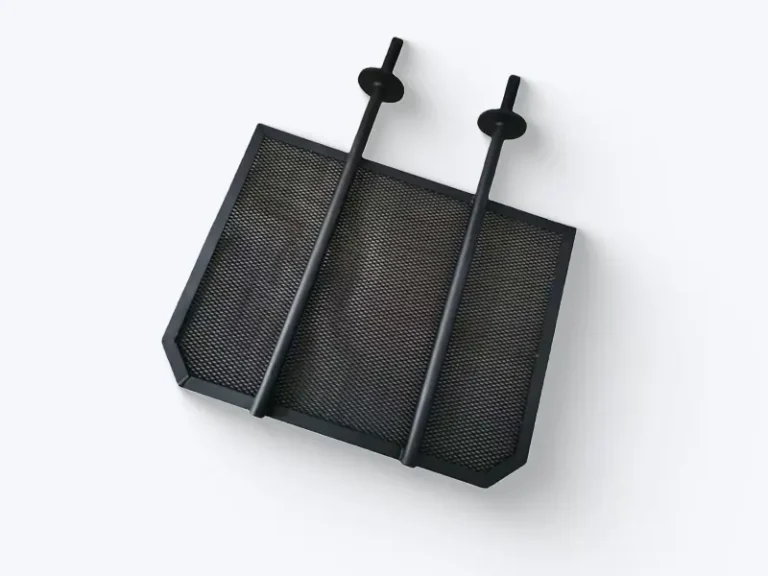
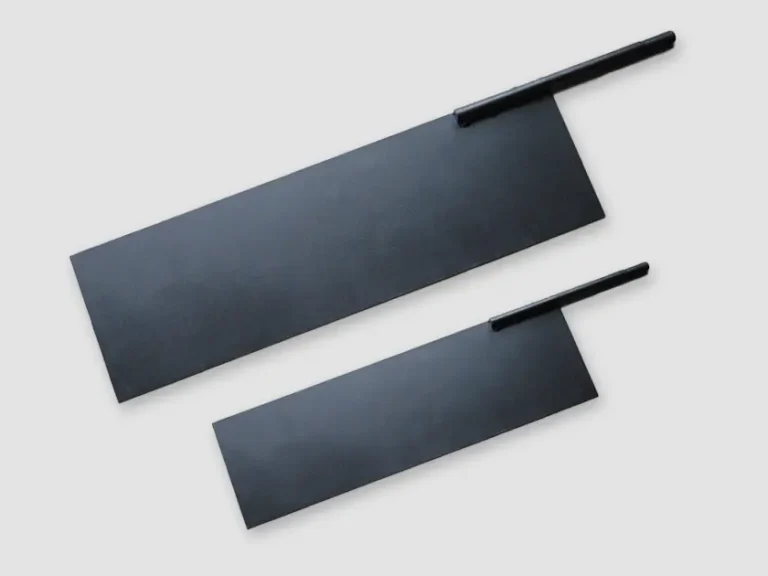
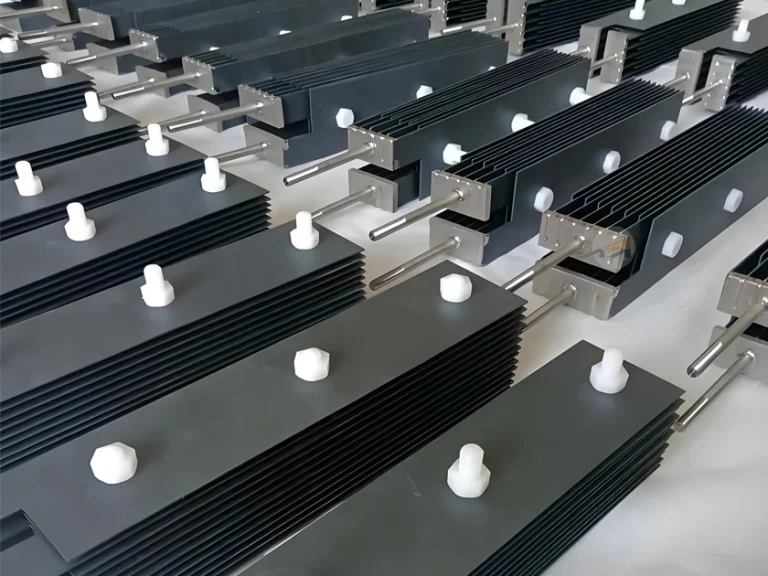
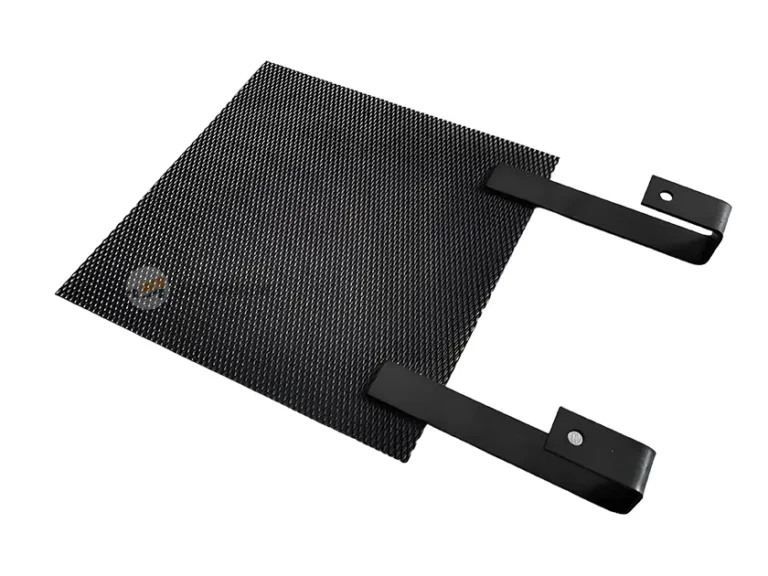
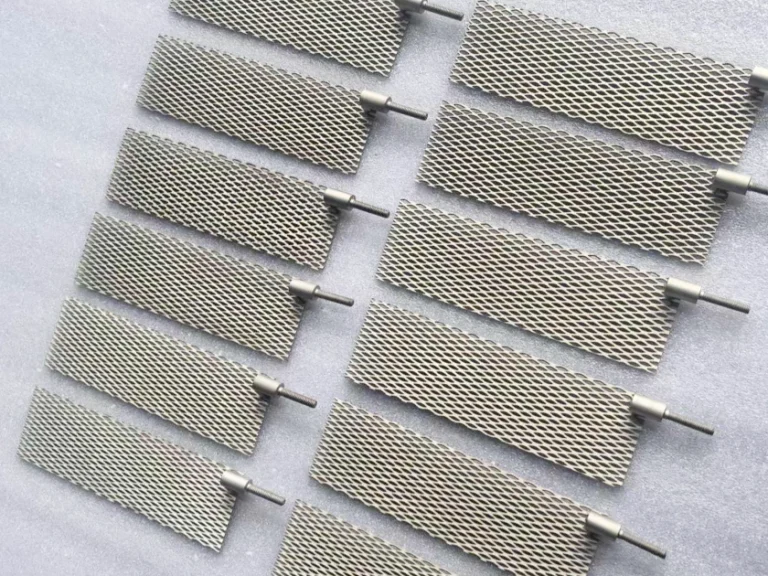
Coated titanium anodes
Coated titanium anodes catalyze reactions through the precious metal coating on the titanium surface, enabling electron transfer and ion migration, thereby completing specific electrochemical processes.


Working Principle of Coated Titanium Anodes
When a coated titanium anodes is connected to a DC power source, it becomes the anode (oxidation electrode) in the electrolytic cell, attracting anions in the electrolyte to move toward it. In this process, the titanium substrate provides physical support for the coating. Additionally, because it easily forms a dense oxide film (TiO₂) in the electrochemical environment, it can effectively prevent itself from being corroded by the electrolyte, ensuring the structural stability of the titanium anode. The noble metal oxide coating on the surface, such as oxides of ruthenium (RuO₂), iridium (IrO₂), platinum (Pt), etc., acts as a catalyst for the reaction. Take the chlorine evolution reaction occurring in an electrolyte containing chloride ions as an example.
Reaction formula:2Cl⁻→Cl₂↑ + 2e⁻
The active sites in the coating can adsorb chloride ions (Cl⁻) and promote them to lose electrons, which are oxidized to form chlorine gas (Cl₂). In this process, electrons transfer from chloride ions to the anode, then flow to the negative electrode of the power supply through the external circuit, thereby forming a current loop. In oxygen-containing electrolytes, such as acidic or neutral solutions, the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) may occur.
Reaction formula: 2H₂O→O₂↑ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻
The coating also catalyzes the decomposition of water molecules, generating oxygen and hydrogen ions.
During the electrochemical reaction process, ion migration is also an important link. Under the action of an electric field, cations move toward the cathode, while anions move toward the anode. This directional migration of ions ensures the charge balance in the electrolyte and maintains the continuous progress of the electrochemical reaction.
The high conductivity of the coated titanium anodes ensures that the current can be evenly distributed on the anode surface, avoiding local overheating or uneven reactions, thereby improving electrolysis efficiency and reaction stability.
Structure of Coated Titanium Anode
Coated titanium anodes are mainly composed of two parts: substrate materials and coating materials. The properties of these two parts of materials complement each other and jointly determine the performance of titanium anodes.
- The base materials are industrial pure titanium grades Gr1 and Gr2. Titanium has high mechanical strength, which enables it to withstand various external forces encountered during production, installation, and use, and is not prone to deformation or damage, providing a solid and reliable support for the coating.
- The coating material is composed of precious metal oxides (such as platinum, ruthenium, iridium, etc.) and non-precious metal oxides (such as tin, tantalum, etc.) in a certain proportion. These oxides are coated on the surface of the titanium substrate through a specific process to form a thin film with electrocatalytic activity. It has excellent electronic conductivity, which effectively reduces the overpotential of redox reactions, such as oxygen evolution and chlorine evolution reactions, thereby accelerating the progress of electrochemical reactions and improving electrolysis efficiency.
The composition of the coating is not fixed; instead, it is flexibly adjusted according to the specific operating environment and electrolysis requirements. In situations where oxygen evolution is needed, titanium anodes may use mixed metal oxide electrodes with iridium dioxide as the main component; in chlorine evolution applications, coated formulations such as ruthenium-titanium or ruthenium-iridium-titanium may be selected to meet different electrolysis requirements.
Coated titanium anodes
One promising area of research involves the exploration of novel materials for anode coatings. Current coatings, often composed of platinum or mixed metal oxides, can be expensive and face limitations in specific environments. By investigating alternative materials, such as non-precious metals and advanced polymers, researchers aim to develop cost-effective solutions that do not compromise performance. These innovations could lead to wider adoption of titanium anodes across different industries, thereby reducing dependence on less efficient and environmentally harmful materials.
Moreover, the integration of nanotechnology into the production of coated titanium anodes holds great potential. The manipulation of materials at the nanoscale can enhance surface area and reactivity, resulting in improved current efficiency and longer lifespans for anodes. This trend may also pave the way for multifunctional properties, enabling coated titanium anodes to serve additional purposes beyond electrochemical reactions. For instance, incorporating photonic properties may allow these anodes to harness solar energy in conjunction with electrochemical processes, creating hybrid systems that address the dual challenges of energy generation and corrosion resistance.
Additionally, advancements in manufacturing technologies, such as additive manufacturing and 3D printing, will likely revolutionize the design and production processes of titanium anodes. These innovative techniques can facilitate the creation of complex geometries and tailored designs that optimize performance for specific applications. As the demand for more efficient and durable coated titanium anodes grows, the collaboration between researchers and industry professionals will become crucial in shaping the future landscape of this technology.


Future Trends in Coated Titanium Anodes Technology
The field of titanium anode technology is poised for significant advancements due to ongoing research in materials science and engineering. As industries increasingly emphasize sustainability and efficiency, the development of coated titanium anodes is expected to play a pivotal role. Future innovations may lead to enhanced coatings that improve the electrochemical performance and durability of titanium anodes in a variety of applications, including marine, electrochemical, and industrial sectors.
One promising area of research involves the exploration of novel materials for anode coatings. Current coatings, often composed of platinum or mixed metal oxides, can be expensive and face limitations in specific environments. By investigating alternative materials, such as non-precious metals and advanced polymers, researchers aim to develop cost-effective solutions that do not compromise performance. These innovations could lead to wider adoption of titanium anodes across different industries, thereby reducing dependence on less efficient and environmentally harmful materials.
Moreover, the integration of nanotechnology into the production of coated titanium anodes holds great potential. The manipulation of materials at the nanoscale can enhance surface area and reactivity, resulting in improved current efficiency and longer lifespans for anodes. This trend may also pave the way for multifunctional properties, enabling coated titanium anodes to serve additional purposes beyond electrochemical reactions. For instance, incorporating photonic properties may allow these anodes to harness solar energy in conjunction with electrochemical processes, creating hybrid systems that address the dual challenges of energy generation and corrosion resistance.
Additionally, advancements in manufacturing technologies, such as additive manufacturing and 3D printing, will likely revolutionize the design and production processes of titanium anodes. These innovative techniques can facilitate the creation of complex geometries and tailored designs that optimize performance for specific applications. As the demand for more efficient and durable coated titanium anodes grows, the collaboration between researchers and industry professionals will become crucial in shaping the future landscape of this technology.
Coated titanium anodes have emerged as a paramount innovation in the field of electrochemistry, effectively transforming various applications from industrial processes to environmental conservation. Their development over the years reflects significant advancements in materials science, particularly with respect to corrosion resistance, durability, and overall efficiency. This technology has not only enhanced performance in electrochemical cells but has simultaneously contributed to sustainability initiatives within multiple industries.
The role of coated titanium anodes in sectors such as wastewater treatment, metal plating, and even energy production cannot be overstated. Their inherent properties enable longer operational lifespans and reduce the need for frequent replacements, thus decreasing overall material consumption and waste generation. This aspect aligns with global sustainability goals, making them a forward-thinking choice in manufacturing and environmental stewardship.
Furthermore, the diverse range of applications demonstrates the versatility of these anodes. From cathodic protection to electrolysis, coated titanium anodes have proven to be effective across different environments and conditions. Organizations that prioritize innovation and sustainability stand to benefit immensely from integrating these anodes into their operations, improving efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.
As industries continue to evolve and face the challenges of resource management and pollution control, the role of coated titanium anodes will likely expand. Their adoption represents a step toward more sustainable practices in electrochemical processes, thereby highlighting their significance in shaping a more responsible future for relevant sectors. The continued research and development in this field promise further enhancements and adaptation of coated titanium anodes, ensuring their relevance in meeting the emerging needs for sustainable solutions.
Coated titanium anodes manufacturer from China
Qixin Titanium is a manufacturer of titanium anodes from China., focusing on the R&D, manufacturing and application of coated titanium anodes.
Qi Xin Titanium was founded in 2006., with over 20 years of manufacturing experience, we provide stable and reliable titanium anode products suitable for multiple scenarios. We help enterprises improve electrolysis efficiency, reduce operating costs, and offer personalized customization to ensure long-term stable operation.